ENERGY QUANTIZATION AND DUALITY OF MATTER
CONTENT
- Energy Levels in an Atom
- Ground State and Excited State
- Emission of Light Energy on Return to Ground State
- Photo-electric Emission
- Einstein’s Photo-electric Equation and its Explanation
- X-ray Production
- Characteristics and Properties of X-ray
- Uses of X-ray
- Duality of Matter-wave
- Wave-Particle Paradox
- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Energy Levels in an Atom
Electrons in atoms exist in certain energy levels. They can jump from one energy level to another by gaining or losing energy but they are not allowed any energy that lies in between two energy levels. The electrons can only accept or lose certain definite amount of energy. Energy is quantised.
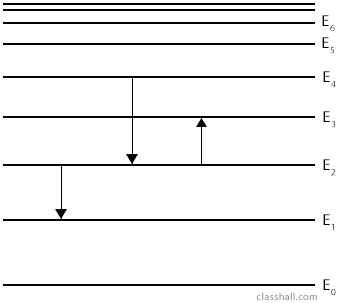
(i) A jump from E2 to E1 will result in emission of photon.
\(hf = E_2 -E_1\)
(ii) A jump from E4 to E2 will result in emission of photon.
\(hf = E_4 -E_2\)
(iii) A jump from E2 to E3 will be as a result of absorption of photon of energy.
You are viewing an excerpt of this lesson. Subscribing to the subject will give you access to the following:
- NEW: Download the entire term's content in MS Word document format (1-year plan only)
- The complete lesson note and evaluation questions for this topic
- The complete lessons for the subject and class (First Term, Second Term & Third Term)
- Media-rich, interactive and gamified content
- End-of-lesson objective questions with detailed explanations to force mastery of content
- Simulated termly preparatory examination questions
- Discussion boards on all lessons and subjects
- Guaranteed learning