EQUILIBRIUM OF BODIES IN LIQUIDS
CONTENT
- Equilibrium of Bodies in Liquids
- Archimedes’ Principle
- The Density of a Body
- Relative Density
- The Principle of Floatation
- Applications of the Principle of Floatation
- Practice Exercises
Equilibrium of Bodies in Liquids
Boat, ship or a swimmer can float on water. This is as a result of certain forces acting on these bodies.
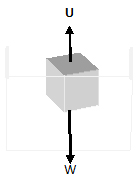
Consider a cube floating in water as shown below. For the cube to be in equilibrium U = W
The force U is called the upthrust.
Upthrust can be defined as an upward force experienced by an object in a fluid.
Upthrust can also be defined as the loss of weight experienced by an object partially or completely immersed in a fluid. for object floating in a fluid,
\(weight = upthrust \\ W = U\)
For object partly or wholly immersed in a fluid, (e.g bucket of water inside the water in a well weight lighter than )
U = weight loss
Consider a bucket of water of weight W in a well which is held by a string whose tension is T.
You are viewing an excerpt of this lesson. Subscribing to the subject will give you access to the following:
- NEW: Download the entire term's content in MS Word document format (1-year plan only)
- The complete lesson note and evaluation questions for this topic
- The complete lessons for the subject and class (First Term, Second Term & Third Term)
- Media-rich, interactive and gamified content
- End-of-lesson objective questions with detailed explanations to force mastery of content
- Simulated termly preparatory examination questions
- Discussion boards on all lessons and subjects
- Guaranteed learning