EXPLANATION OF MELTING, BOILING AND EVAPORATION USING KINETIC THEORY
Content:
- Melting
- Boiling
- Evaporation
- Differences between Boiling and Evaporation
- Factors Affecting Evaporation
Melting
When a solid is melting, the particles acquire more kinetic energy and vibrate more vigorously. Eventually, at a certain temperature called the melting point of the solid, the force of the vibration overcomes the binding force and the solid structures collapse. The particles are no longer held in fixed positions but are ready to move about. At this point, the solid is said to have melted or liquefied.
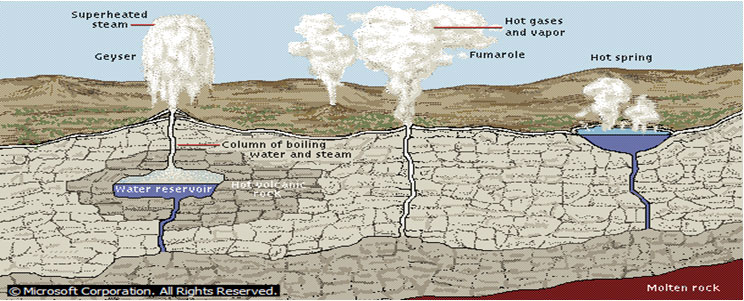
Formation of Geysers
Geysers are caused when underground chambers of water are heated to the boiling point by volcanic rock. When heat causes the water to boil, pressure forces a superheated column of steam and water to the surface. Because most geothermal reservoirs are capped by overlying rock, the heated water cannot escape, remaining underground instead. If a geothermal reservoir is sufficiently close to the surface, the heated water can be piped to the surface and used to produce energy.
- NEW: Download the entire term's content in MS Word document format (1-year plan only)
- The complete lesson note and evaluation questions for this topic
- The complete lessons for the subject and class (First Term, Second Term & Third Term)
- Media-rich, interactive and gamified content
- End-of-lesson objective questions with detailed explanations to force mastery of content
- Simulated termly preparatory examination questions
- Discussion boards on all lessons and subjects
- Guaranteed learning