GIANT MOLECULES – CARBOHYDRATES
CONTENT
- Sugars (Carbohydrates)
- Classification of Carbohydrates
- Sources of Sugars
- Reducing and Non-reducing Sugars
- Hydrolysis of Sucrose and Starch
- Test for Starch and Sugars
- Uses of Starch and Glucose
Sugars
Carbohydrates are organic compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in which the ratio of atoms of hydrogen and oxygen is 2:1.
The general molecular formula of carbohydrate is Cx(H2O)y or CxH2yOy
Classification of Carbohydrates
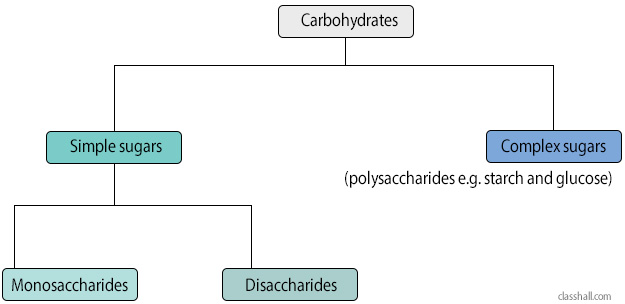
The classification is based on the effect of acid hydrolysis of carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides
These are simple sugars. Examples are glucose and fructose. They cannot be split into simple molecules by acid hydrolysis.
Structure of Glucose and Sucrose
Disaccharides
They are also sugars e.g. sucrose, maltose, and lactose. They can be split into two molecules of monosaccharide by acid hydrolysis.
You are viewing an excerpt of this lesson. Subscribing to the subject will give you access to the following:
- NEW: Download the entire term's content in MS Word document format (1-year plan only)
- The complete lesson note and evaluation questions for this topic
- The complete lessons for the subject and class (First Term, Second Term & Third Term)
- Media-rich, interactive and gamified content
- End-of-lesson objective questions with detailed explanations to force mastery of content
- Simulated termly preparatory examination questions
- Discussion boards on all lessons and subjects
- Guaranteed learning