PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS - WOOD
CONTENT
- Definition of Materials
- The Definition of Wood
- Identification of Wood
- Classification and Properties of Wood
- Differences in the Properties of Hardwood and Softwood
- Properties of Materials and Identification of Wood, Timber, Structure of Wood
- The Growth of Timber and Wood Structure
- Five Main Parts Cross Section, Classes and Properties
Definition of Materials
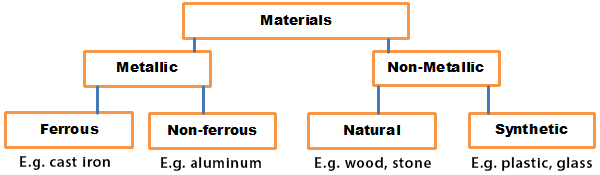
Materials are substances from which other things can be made. Basically, they can be classified into two: metallic and non-metallic. Furthermore, the metallic ones can be subdivided into ferrous and non-ferrous metals, while the non-metallic ones can be divided into natural and synthetic materials.
The Definition of Wood
One of the materials that is supplied by nature is wood. Wood is commonly used in some engineering manufacture because it is light, strong and can be worked upon easily.
Wood is a material obtained from trees. It is made up of cellulose and lignin each consisting of 60% and 28% respectively.
Identification of Wood
Generally, wood has very good combination of colours to give it high decorative value. This makes it possible to identify some woods by their colour. Examples are:
| S/N | Trees | Colour Identification | ||
| 1 | Iroko | Yellowish brown | ||
| 2 | Mahogany | Reddish brown | ||
| 3 | Afara | Pale-colour | ||
| 4 | Teak | Reddish brown | ||
| 5 | Yew | Dark-green | ||
| 6 | Cotton-wood | Grayish white to light grayish brown | ||
| 7 | Hickory | Reddish brown | ||
- NEW: Download the entire term's content in MS Word document format (1-year plan only)
- The complete lesson note and evaluation questions for this topic
- The complete lessons for the subject and class (First Term, Second Term & Third Term)
- Media-rich, interactive and gamified content
- End-of-lesson objective questions with detailed explanations to force mastery of content
- Simulated termly preparatory examination questions
- Discussion boards on all lessons and subjects
- Guaranteed learning