THE ORGAN OF TASTE
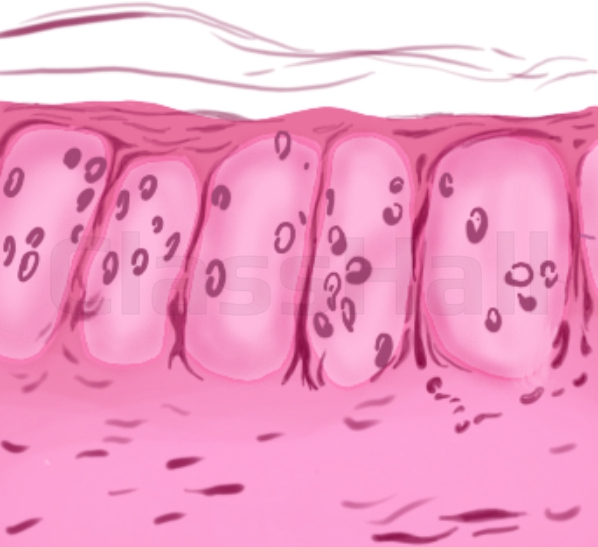
In mammals the organ of taste is the tongue. Taste chemoreceptors are grouped on the upper surface of the tongue, on the soft palate and in the epithelium at the back of the mouth. These chemoreceptors are specialized sense cells that synapse with sensory neurones. On the tongue they are found in the taste buds. Taste buds lie in grooves on the surface of the tongue. Substances have to be in dissolved form to stimulate the taste receptors.
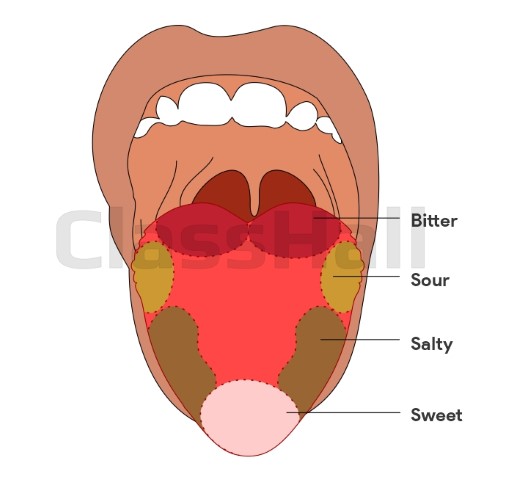
The tongue is sensitive to four primary tastes – sweat, sour, salty and bitter. The back of the tongue is sensitive to bitter taste; the sides to salty and sour stimuli while the tip is sensitive to sweet sensations. The tongue can also detect alkaline taste, texture of food as well as its temperature.
Taste Receptors
 Taste buds in the tongue
Taste buds in the tongue
EVALUATION
- State the 4 types of sensation the tongue is sensitive to and the sections of the tongue that respond to these sensations.
- Briefly discuss the organ of taste.
- NEW: Download the entire term's content in MS Word document format (1-year plan only)
- The complete lesson note and evaluation questions for this topic
- The complete lessons for the subject and class (First Term, Second Term & Third Term)
- Media-rich, interactive and gamified content
- End-of-lesson objective questions with detailed explanations to force mastery of content
- Simulated termly preparatory examination questions
- Discussion boards on all lessons and subjects
- Guaranteed learning