THE SENSE ORGANS
CONTENT:
- The Eye
- The Ear
- The Nose
- The Tongue
- The Skin
- The Nervous System
- Reflex Action
We respond to changes or stimuli in our environment through the sense organs. Sense organs are parts of our body which include the eye, ear, nose, tongue and skin. These are organs that link us with our environment.
The Eye
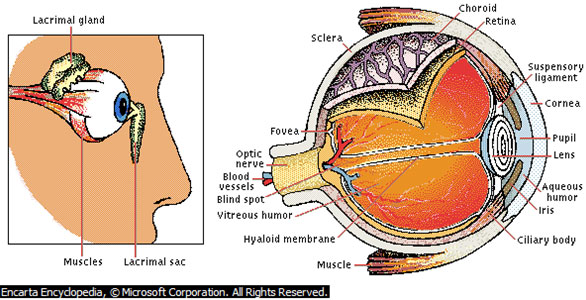
Structure of the Eye
The amount of light entering the eye (right) is controlled by the pupil, which dilates and contracts accordingly. The cornea and lens, whose shape is adjusted by the ciliary body, focus the light on the retina, where receptors convert it into nerve signals that pass to the brain. A mesh of blood vessels, the choroid, supplies the retina with oxygen and sugar. Lacrimal glands (left) secrete tears that wash foreign bodies out of the eye and keep the cornea from drying out. Blinking compresses and releases the lacrimal sac, creating a suction that pulls excess moisture from the eye’s surface.
The eye enables us to see things around us such as size, colour etc.
- NEW: Download the entire term's content in MS Word document format (1-year plan only)
- The complete lesson note and evaluation questions for this topic
- The complete lessons for the subject and class (First Term, Second Term & Third Term)
- Media-rich, interactive and gamified content
- End-of-lesson objective questions with detailed explanations to force mastery of content
- Simulated termly preparatory examination questions
- Discussion boards on all lessons and subjects
- Guaranteed learning