CONTENT
(c) Application of trigonometric ratios (angle of elevation and depression; bearing).
(d) Trigonometric ratios related to the unit circle.
(e) Graphs of sines and cosines.
Application of trigonometric ratios (angle of elevation and depression; bearing).
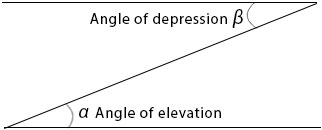
Angle of elevation:
Example 1:
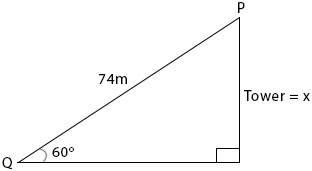
The angle of elevation of a point P on a tower from a point Q on the horizontal ground is 600. If /PQ/=74m, how high is P above the ground?
Solution:
The relevant sides to 600 are Opp and Hyp (SOH)
\(Sin 60^o = \frac{x}{74} \\ \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} = \frac{x}{74} \\ x = \frac{74\sqrt{3}}{2} \\ ∴ x = 37\sqrt{3}m\)
Example 2:
A man 1.8m tall observes a bird on top of a tree. If the man is 21m away from the tree and his angle of sighting the bird is 300, calculate the height of the tree.
Solution:
\(Tan 30^o = \frac{k}{21} \\ k = 21 tan 30^o \\ k = 12.12m\)
Thus height of the tree \(= k + 1.8m \\ = 12.12m + 1.8m = 13.92m \)
Angle of depression:
Example 3:
A boat can be sighted at the sea 71.5m from the foot of a cliff which is 26m high.
- NEW: Download the entire term's content in MS Word document format (1-year plan only)
- The complete lesson note and evaluation questions for this topic
- The complete lessons for the subject and class (First Term, Second Term & Third Term)
- Media-rich, interactive and gamified content
- End-of-lesson objective questions with detailed explanations to force mastery of content
- Simulated termly preparatory examination questions
- Discussion boards on all lessons and subjects
- Guaranteed learning